Introduction
In the era of digital transformation, where real-time data processing and low latency are critical, edge computing has emerged as a revolutionary technology paradigm. Edge computing moves computation closer to the data source – at the very edge of the network – than typical cloud computing, which concentrates data processing in remote data centres. The emergence of tiny mobile data centres (MMDCs) is a major factor facilitating this change. These compact, portable, and highly efficient data centers are driving the adoption and effectiveness of edge computing solutions across industries.
Definition
A Micro Mobile Data Center is a compact, self-contained computing facility designed for rapid deployment and mobility. It houses essential IT infrastructure – such as servers, storage, and networking equipment – within a small, transportable unit, enabling businesses to bring data processing closer to the edge or remote locations for improved performance, flexibility, and scalability.
What Are Micro Mobile Data Centers?
Micro mobile data centers are small-scale, self-contained computing units designed to be deployed quickly and flexibly near the location where data is generated. Unlike traditional data centers – large, static facilities requiring substantial infrastructure – micro mobile data centers are modular, portable, and often housed in ruggedized containers or enclosures. They typically include servers, storage, networking, cooling, and power management systems within a compact footprint.
Key Characteristics of MMDCs:
- Compact size: Often the size of a small cabinet or shipping container, allowing for easy transport and deployment.
- Mobility: Can be mounted on trailers, trucks, or even drones for quick relocation.
- Self-sufficiency: Equipped with integrated power and cooling solutions to operate independently in diverse environments.
- Robustness: Made to endure challenging circumstances like high temperatures, dust, dampness, or vibrations.
- Scalability: Easily scalable by adding or linking multiple units.
What is Edge Computing?
Processing data closer to its source instead of depending on a central cloud is known as edge computing. This approach reduces latency, bandwidth usage, and dependency on centralized infrastructure, enabling faster decision-making and better performance in applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and AR/VR.
Why Edge Computing Matters
- Low latency: Critical for applications where milliseconds count (e.g., industrial automation, autonomous driving).
- Bandwidth savings: Reduces the amount of data that is transferred to the cloud by using local processing and filtering.
- Data privacy and security: Sensitive data can be processed locally, minimizing exposure to cyber risks.
- Reliability: Even in the event of sporadic cloud connectivity, operations can proceed.
Benefits of Micro Mobile Data Centers in Edge Computing
Low Latency and Real-Time Processing:
Their capacity to reduce latency is among MMDCs’ most alluring advantages. By processing data locally, MMDCs eliminate the need to transmit data to distant cloud servers, enabling real-time decision-making. This is essential for applications where judgements can be made in an instant, such industrial automation or driverless cars.
Scalability and Flexibility:
MMDCs are inherently modular and scalable. Organizations can start with a single unit and add more as needed, making them ideal for businesses looking to scale operations without major capital investments. Their mobility means they can be redeployed or reconfigured based on evolving requirements.
Cost Efficiency:
Traditional data centers are expensive to build and maintain. In contrast, MMDCs offer a more cost-effective solution by reducing capital and operational expenditures. Their plug-and-play nature reduces deployment time and infrastructure costs, particularly in locations where building a traditional data center is impractical.
Enhanced Data Security and Compliance:
With data privacy regulations becoming increasingly stringent, MMDCs allow sensitive data to be processed and stored locally, reducing exposure and helping organizations stay compliant with laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. This localized processing minimizes the risk associated with data transfer across borders or insecure networks.
Resilience and Business Continuity:
MMDCs are built to withstand harsh environments and continue functioning during adverse conditions such as natural disasters or power outages. This makes them a vital part of a disaster recovery and business continuity plan, especially for industries that require 24/7 uptime.
Real-World Applications of Micro Mobile Data Centers
Smart Cities:
Smart cities rely on real-time analytics to manage traffic, monitor air quality, and ensure public safety. MMDCs can be deployed across urban environments to support these services by processing sensor data locally and efficiently.
Healthcare:
In remote or rural healthcare settings, MMDCs can be used to store and analyze patient data without needing a reliable internet connection. This facilitates telemedicine, diagnostics, and data sharing while ensuring compliance with health data regulations.
Retail and E-Commerce:
Retailers are using edge computing to personalize customer experiences, manage inventory, and optimize logistics. MMDCs enable localized data processing in stores or warehouses, improving operational efficiency and reducing reliance on centralized systems.
Industrial and Manufacturing:
MMDCs play a critical role in Industrial IoT (IIoT) by collecting and analyzing data from sensors and machines in real-time. This helps manufacturers detect equipment failures, monitor production quality, and improve overall efficiency.
Telecommunications and 5G:
As telecom providers roll out 5G infrastructure, MMDCs are being used to support local cell towers and reduce network latency. These edge nodes handle local traffic processing and content caching, easing the load on central servers.
Challenges and Considerations
While micro mobile data centers offer compelling advantages, there are challenges to consider:
- Power Supply: Ensuring reliable power, especially in remote or off-grid locations, may require integrating renewable energy or backup generators.
- Maintenance: Remote deployments can complicate hardware maintenance and upgrades.
- Network Integration: Seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure and cloud platforms is critical for hybrid edge-cloud architectures.
- Cost: While smaller than traditional data centers, the initial investment and operational costs can be significant depending on scale and complexity.
Future Trends of Micro Mobile Data Center Market
Integration with 5G Networks:
As 5G deployment accelerates globally, micro mobile data centers will become vital for enabling ultra-low latency and high-bandwidth services. Telecom providers are expected to increase investment in MMDCs to support edge computing for applications like AR/VR, autonomous vehicles, and real-time analytics.
AI-Enhanced Edge Processing:
Future MMDCs will increasingly integrate AI chips and machine learning capabilities to handle complex workloads at the edge. This will allow faster data analysis and decision-making without relying on cloud connectivity, especially in mission-critical environments.
Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Designs:
With rising focus on green IT, manufacturers are developing MMDCs with energy-efficient cooling systems, renewable energy compatibility, and low-power hardware. These sustainability features will drive adoption in both urban and remote deployments.
Expansion in Remote and Rural Areas:
MMDCs are being used by businesses and governments to close the digital divide. These portable data centers are ideal for extending network coverage, education, and healthcare services in underserved regions where traditional infrastructure is lacking.
Growth in Modular and Scalable Solutions:
The demand for customizable and modular MMDCs is increasing. Businesses want solutions that can scale with their needs, allowing rapid deployment of additional units or upgraded capabilities without overhauling existing infrastructure.
Micro Mobile Data Center Market Growth Rate
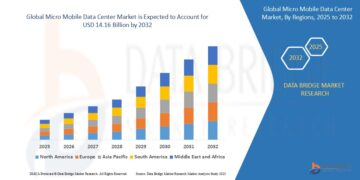
According to Data Bridge Market Research, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.10 percent, the global micro mobile data center market is projected to grow from its 2024 valuation of USD 5.29 billion to USD 14.16 billion by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-micro-mobile-data-center-market
Conclusion
Micro mobile data centers represent a transformative shift in IT infrastructure, perfectly complementing the needs of edge computing. By bringing computing power closer to the source of data, these compact and portable units enable faster, more secure, and more reliable data processing. From telecommunications and industrial IoT to healthcare and emergency response, MMDCs are powering the next generation of digital innovation.