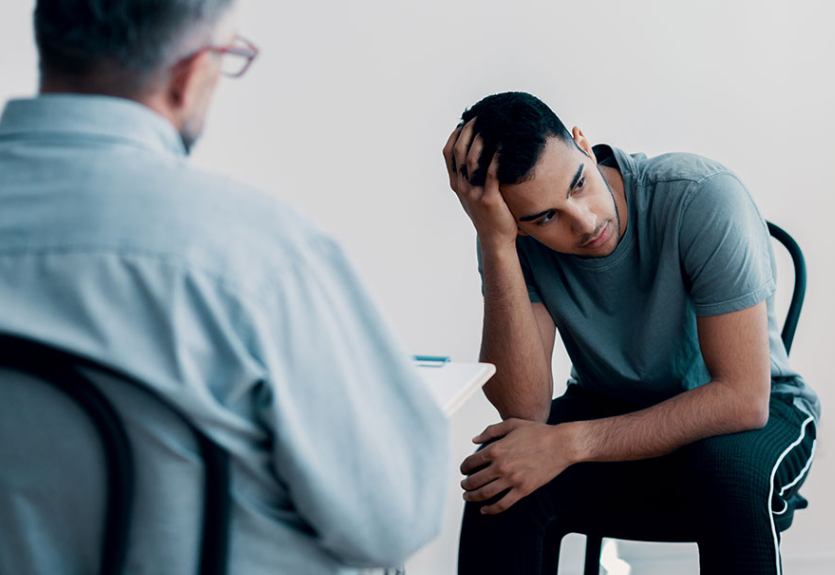
Recovering from addiction is a significant and commendable step toward a healthier life. However, it often comes with emotional and psychological challenges, one of the most common being addiction recovery anxiety. This form of anxiety typically arises when individuals are adapting to life without substances that previously numbed their emotions or served as coping mechanisms. Whether recovering from alcohol, opioids, or other substances, the absence of those chemicals in the body can expose deep-seated stress and unprocessed emotions.
Addiction recovery anxiety can manifest as restlessness, irritability, difficulty sleeping, and constant worry about relapse. Recognizing and addressing this anxiety is crucial for maintaining long-term sobriety and improving overall well-being.
Why Anxiety Is Common During Recovery
There are several reasons why anxiety frequently appears during recovery:
- Neurochemical Imbalance: Prolonged substance use, such as alcohol addiction, alters the brain’s chemistry. Once use stops, the brain needs time to rebalance neurotransmitters responsible for mood and stress.
- Emotional Reawakening: Without substances to mask emotions, individuals may face unresolved trauma or painful memories, which can trigger anxiety.
- Fear of the Future: Worries about maintaining sobriety, repairing relationships, or returning to work can create overwhelming stress.
- Physical Symptoms: Withdrawal symptoms and the body’s adjustment can also contribute to heightened anxiety levels.
Practical Strategies to Manage Anxiety in Recovery
1. Develop a Structured Routine
Structure is a key component in addiction recovery. Creating a daily schedule that includes meal times, exercise, therapy, and rest helps minimize unpredictability, which can often fuel anxiety. A structured routine fosters a sense of control and stability, both of which are essential for reducing stress.
2. Practice Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation, deep breathing, and grounding techniques, can help calm the mind and refocus attention on the present moment. Regular mindfulness practice has been proven to lower anxiety levels, reduce cravings, and improve emotional regulation.
3. Engage in Physical Activity
Exercise is a natural anxiety reliever. Activities like walking, swimming, yoga, or even dancing release endorphins, the body’s feel-good hormones, which can alleviate anxiety and boost mood. Establishing a regular exercise routine also improves sleep, concentration, and self-esteem.
4. Seek Professional Support
Therapists and counselors trained in addiction recovery can provide invaluable support in managing anxiety. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), for example, helps individuals identify and reframe negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. Group therapy and support groups also offer community support and shared coping strategies.
5. Focus on Nutrition and Sleep
Nutrition and rest play a foundational role in mental health. Poor diet and lack of sleep can exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Prioritize a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and aim for consistent, restful sleep to support the body’s recovery process.
6. Limit Caffeine and Sugar Intake
Stimulants like caffeine and sugar can increase anxiety, especially in individuals who are already experiencing emotional volatility during recovery. Reducing or eliminating these substances can help stabilize mood and energy levels.
7. Journal Your Thoughts and Feelings
Writing down your thoughts can be a therapeutic way to release stress and reflect on your progress. Journaling helps identify anxiety triggers and encourages positive self-reflection, allowing individuals to track their emotional growth over time.
8. Build a Support Network
Having a network of friends, family, or recovery peers provides emotional security and encouragement. A strong support system can offer perspective, accountability, and empathy—all of which are critical when dealing with anxiety in recovery.
Conclusion:
Managing addiction recovery anxiety is not just about reducing symptoms; it’s about building a lifestyle that supports emotional resilience and long-term sobriety. By integrating daily routines, professional support, and self-care techniques, individuals can face recovery with confidence and clarity. For those dealing with alcohol addiction or other substance dependencies, these strategies are essential for healing and growth. If anxiety becomes overwhelming or persistent, seeking professional addiction treatment is a vital step toward recovery and long-term well-being.